Debt settlement, in which you pay off a debt by paying less than you owe, will hurt your credit scores, but it’s better than not paying it at all. Itâs worth exploring alternatives before seeking debt settlement.
Debt settlementânegotiating forgiveness of a financial obligation in exchange for partial repaymentâcan ease financial burdens, but it will harm your credit. And, if you hire a so-called debt-relief company to help, it will likely be expensive.
Should you decide to negotiate a settlement on your own to save money on fees, you should still be aware that it is risky to do so. For starters, creditors may refuse to work with you (or any company you hire) to settle your debt. Also, reaching a debt settlement often involves racking up delinquent payments that damage credit scores. And settling an account instead of paying it in full is seen as negative because the creditor agreed to take a loss in accepting less than what it was owed.
Not having a debt on your credit report is better than having it marked as “settled in full.” But it’s still not ideal, and it will probably hurt your credit score. It’s better for your credit if you can pay off all of your debts at once.
What Does Settled in Full Mean?
When you are unable to pay a debt in full, you may be able to negotiate a settlement with the creditor. This involves agreeing to pay a portion of what you owe in exchange for having the remaining balance forgiven.
If you successfully complete the agreed-upon settlement payments, the creditor will update your account status to show “settled in full.” This signals that while you didn’t pay back the entire amount owed, your obligation to the creditor is considered fulfilled.
Settling a debt means you paid less than the full balance Creditors will sometimes accept settlement offers if a borrower has fallen significantly behind on payments and it seems unlikely the full amount will ever be repaid
How Does a Settled Debt Affect Your Credit?
Having an account listed as settled on your credit report indicates you are a risky borrower. While better than default, it will still damage your credit score.
-
The most important part of your credit score is your payment history, so missing payments before a settlement will hurt your score. To get more power in negotiations, many settlement programs require people to stop making payments.
-
Also, settling shows that you haven’t handled your debts well in the past. This raises questions about your reliability for future debts.
-
On the plus side, settling and paying less lowers your overall outstanding balances. This helps improve your credit utilization ratio.
The impact on your score depends on your full credit profile. But you can expect at least a moderate decline compared to if you paid in full. A settled account stays on your report for 7 years.
Is Settled in Full Bad for Your Credit Score?
Settling isn’t ideal and will likely reduce your credit score. But it also gets rid of the debt burden and prevents further damage from escalating delinquencies or charge-offs.
If you are facing financial hardship, settling troubled accounts may actually be the best option to start rebuilding your credit. Just be sure to weigh the pros and cons first.
Pros of Settling Debt:
- Resolve account for less than you owe
- Avoid additional missed payments
- Improve credit utilization ratio
- Prevent worse outcomes like default
Cons of Settling Debt:
- Remains on credit report for 7 years
- Signals you are a risky borrower
- Will likely lower your credit score
- Can only settle very delinquent accounts
In general, try to pay off all of your debts as soon as you can. But also know when you need more freedom because of your finances. In some situations, it may be best to settle for less than what is owed.
Alternatives to Settling Your Debt
Before agreeing to a settlement that will stay on your credit history, explore some other options:
1. Negotiate with creditors – Ask about hardship programs to reduce or defer payments until you recover financially. This prevents settlement.
2. Use credit counseling – Nonprofit agencies can help manage payments and negotiate with creditors. Many offer debt management plans.
3. Take out a debt consolidation loan – These loans allow you to pay off multiple debts under one new loan with better terms.
4. File for bankruptcy – This is a last resort if you truly can’t repay debts. While damaging, its impact on your credit fades over time.
5. Request goodwill deletion – You may be able to get the creditor to remove a settled account if you plead financial hardship. Get any agreements in writing.
When Is Debt Settlement Your Best Option?
According to financial experts, debt settlement may make sense if:
- You owe more than half your annual income in debt
- Your credit score is already low from missed payments
- You don’t qualify for other debt relief programs
- Bankruptcy would be too damaging for your situation
While a last resort, settling troubled accounts is sometimes the most practical path back to financial health. Evaluate all facets of your situation carefully before making a decision.
Can a Settled Debt Show As Paid in Full?
It is sometimes possible to negotiate having a settled debt reported as paid in full instead. This requires persuading the creditor to overlook the settlement and mark your account as fully paid.
Creditors have no obligation to report settled debts this way. But it doesn’t hurt to ask politely if a settlement is your only good option. Get any agreement to change the credit reporting in writing.
Showing as paid in full allows you to avoid the consequences of a settlement on your credit score and report. However, most lenders will stick to reporting settled accounts accurately. So manage your expectations.
Key Takeaways on Settled in Full Status
-
Settled means you paid less than you owed in exchange for closing out the debt.
-
Settlements hurt your credit score by signaling you are high-risk.
-
If possible, find alternatives to settling that let you pay in full.
-
Under certain circumstances, settling troubled debts can help more than it hurts.
-
Try asking creditors to report settled debt as paid in full instead.
Ideally, you should meet all financial obligations in a timely manner. But life isn’t always ideal. While damaging, settling debts is sometimes the only realistic option during financial crises. Consider both the credit implications and your unique situation before making settlement decisions.
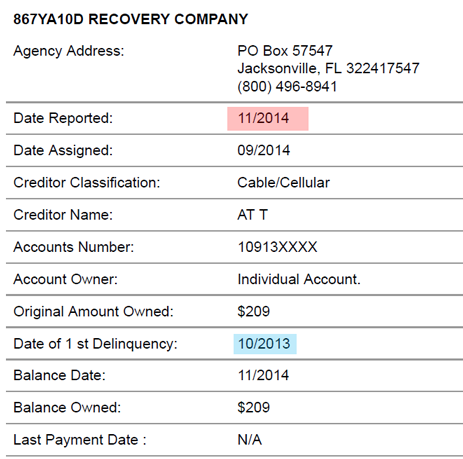
How to Avoid Debt Settlement
If you feel unable to repay a debt in full, there may be better alternatives than debt settlement. These options are worth considering:
If your credit is good, debt consolidation can bring relief from high-interest debt. Using proceeds of a personal loan or home equity loan with a relatively low interest rate to pay off multiple high-interest card accounts can bring significant savings in interest charges.
Replacing multiple credit card bills, with minimum payment requirements that change each month, with a single, predictable fixed payment also can make budgeting easier. Just make sure you dont run up new credit card balances.
A debt management plan (DMP) is a repayment plan arranged by a nonprofit credit counseling agency. Under this arrangement, the agency reviews your finances, helps devise a payment plan you can afford and then works with creditors to arrange for repayment over time. You make one monthly payment to the credit counseling agency, and they distribute payments to your creditors.
The agency often charges a modest upfront fee and collects additional fees from your payments, but costs typically are less than youd pay a for-profit debt-relief company. Note that credit card issuers may require you to close the accounts that are part of your DMP, limiting your access to credit and potentially hurting your credit scores. The National Foundation for Credit Counseling and the Financial Counseling Association of America provide lists of reputable, certified nonprofit credit counselors who can help you set up a DMP.
If a temporary financial hardship is making it hard to pay your debt, lenders may be willing to extend forbearance. This is a short-term reduction or suspension of your monthly payments and/or a waiver on interest charges and fees.
Lenders typically only grant this option if asked and limit it to borrowers with good credit who can show that theyll be able to resume regular payments within six to 12 months. This option will extend the amount of time it takes to repay your debt, however.
In a loan modification (also called a workout agreement when applied to credit cards), the lender permanently restructures your borrowing terms. The goal is to make monthly payments more affordable, but it may have other, less appealing consequences. Credit card issuers may reduce your borrowing limit, while issuers of installment loans may extend your borrowing term, adding extra payments over the life of the loan and increasing your total interest costs.
Why Settling an Account Is Better Than Not Paying at All
Despite the potential downside, settling a debt by making partial repayment is better for your credit (and peace of mind) than neglecting it and leaving it unpaid. If you ignore a debt, the creditor will typically turn it over to a collection department or third-party collection agency.
Accounts in collections are typically listed on your credit report and will hurt your credit scores. Whats more, collection agents can be relentless in their use of phone calls and emails seeking payment. They can also sue you and, if successful, garnish your wages, seize your bank accounts or have a lien placed against your property for the amount you owe.
Whats Better For Your Credit Paid In Full or Settled for Less
FAQ
Is it better to be settled or paid in full on credit report?
On a credit report, “paid in full” signifies that the total amount owed on an account, including any interest and fees, has been fully repaid. “Settled” means the creditor agreed to accept less than the full balance to resolve the debt.
Is it better to pay off collections in full or settle?
Settling is often the fastest and most affordable way to clear away these kinds of debts, especially if you’re dealing with multiple debts in collections. May 29, 2025.
Is settlement good for credit score?
A settlement doesn’t negatively affect your credit scores. There is absolutely no difference scorewise between paying in full or settling for a lesser amount. The account will stay on your reports for 7 years from the date the account first went delinquent.
Can I remove settled debts from my credit report?
Generally, settled debts can’t be removed from your credit report if the information is accurate. However, there are ways to potentially improve your credit score related to settled debts. You can dispute errors, negotiate a “pay-for-delete” agreement with the creditor, or request a “goodwill deletion”.
