How Much Income Do You Need to Qualify for a $200,000 Mortgage?
To get approved for a $200,000 mortgage, you need to carefully plan and prepare your finances. As a mortgage lender, I’m often asked, “How much income do I need to qualify for a $200,000 mortgage?” There isn’t a single answer that works for everyone, but this article will go over the main things lenders look at when approving these kinds of loans.
The Primary Factors That Impact Mortgage Qualification
When determining your eligibility for a mortgage, lenders mainly look at two key factors – your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) and credit score.
Debt-To-Income Ratio
Your DTI shows how much money you make each month compared to how much you owe each month. Most conventional mortgages require your DTI to be below 50%. Your DTI would be 20% ($2,500 / $5,000), if your total monthly debts are $2,500 and your gross monthly income is $5,000. The lower your DTI, the more likely you are to be approved.
Credit Score
Lenders also look at your credit report and score, which show how well you’ve paid your debts in the past. To get a conventional mortgage, most lenders want scores of at least 620, but many want scores of 680 or higher. The higher your score, the better your chances of approval. FICO and VantageScore are the two main scoring models.
Other Key Criteria
Along with DTI and credit score, lenders determine if you have enough cash reserves, stable employment history, and income sources. Providing tax returns, bank statements, and other financial paperwork helps demonstrate qualification. First-time homebuyers also need 3.5% for a downpayment in most cases.
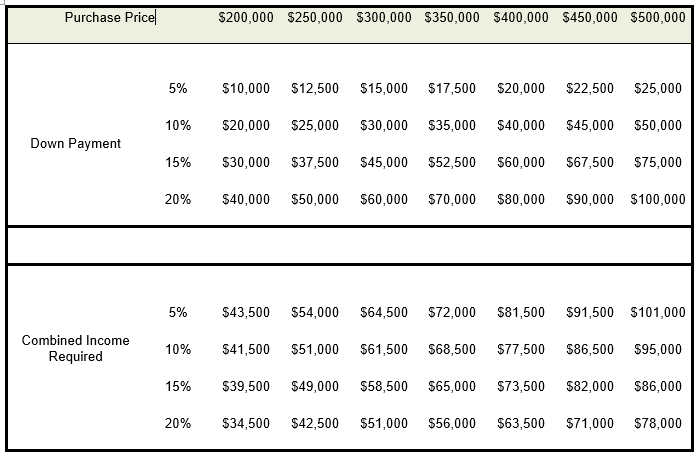
How Much Income You Need for a $200,000 Mortgage
If you don’t have any other big debts, you may need around $60,000 a year in gross income to be able to get a $200,000 mortgage. However, the actual amount can vary significantly depending on your:
-
Downpayment amount – The more you put down, the less you need to borrow. Putting 20% down reduces your required mortgage.
-
Loan program – FHA loans allow higher DTIs and lower scores but require mortgage insurance. VA and USDA loans have flexible qualification guidelines for eligible borrowers.
-
Monthly debts – Less existing monthly debt results in a lower DTI and increases eligibility.
-
Credit score – A higher score within lending guidelines provides better mortgage rates and terms.
-
Location – Required income levels vary by real estate markets across the country. High-cost areas have higher incomes.
I always recommend connecting with an experienced loan officer when starting the mortgage process. They can review your specific scenario and provide a more accurate estimate of the income needed for the mortgage amount, downpayment, and home price you have in mind. Pre-qualification early on also allows you to make any necessary adjustments to debt, credit, and savings to put yourself in a stronger position before applying.
The Bottom Line
While a rough guideline suggests around $60,000 in yearly income may be enough for a $200,000 mortgage, many factors impact your actual qualification requirements. Working with a lender to analyze your unique financial situation is the best way to determine if you have the right income for the mortgage amount that matches your home buying goals.
Loan type and interest rate
The mortgage rate you get and, by extension, the amount you can borrow depend on the type of loan program you choose. The differences tend not to be huge, but every bit helps when you’re paying interest on a large sum over a long time.
Let’s take a single month, as an example that shows those differences.
Here were the average interest rates across three major loan types:
- Conventional loans: %
- FHA loans: %
- VA loans: %
The differences can be even greater if you choose a shorter-term loan (usually, a 10-, 15- or 20-year mortgage) rather than a 30-year mortgage term, or if you opt for an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM).
Income isn’t the only factor for mortgage qualifying
Of course, mortgage lenders take your income into account when deciding how much they are prepared to lend you. For lenders to decide how much of a home loan to give you, income is just one of many things they look at. Other important factors for mortgage qualifying include:
- Credit history: If you have good credit, you can get more loans. You might also be able to get a lower interest rate, which will help you buy a house with more money.
- Debt-to-income ratio (DTI): If you keep your other debts like credit cards and car loans low, you can make more money each month and get a bigger mortgage loan.
- History of employment: Before giving you a home loan, most lenders want to see that you’ve had steady work for two years.
- Capital and savings: These days, you don’t need a lot of savings to get a home loan. If your income is low, however, having “cash reserves” in your bank account might make it easier for you to get a home loan.
- Homeownership costs like property taxes, homeowners insurance, and HOA dues (if you live in a condo or townhome with a homeowners association) will also affect your ability to buy a home. The less you can borrow, the higher your total mortgage payment will be.
You don’t need to be perfect in all these areas to get a home loan. But improving one area of your finances (like your credit report or down payment) can often help make up for a weaker area (like a lower income).
The size of your down payment is an important consideration in your home buying budget. The more money you put down, the smaller your loan amount will be. That can help you qualify if your income is relatively low.
For instance, say you want to buy a $250,000 home. With a 3% down payment, your loan amount is $242,500 and your monthly mortgage payments are about $1,573 (assuming a 6. 75% interest rate). But if you can put 10% down, your loan amount drops to $225,000. Your monthly mortgage payments are over a $100 cheaper. This can make it easier to qualify for the loan payment on your mortgage.
Additionally, those who are financing a home purchase with a conventional loan will pay private mortgage insurance (PMI) when they put less than 20% down. You can get rid of your PMI when there is at least 20% equity in the home. However, for the first several years, you’ll pay these insurance premiums along with your mortgage payment. So again, home buyers with larger down payments can pay less per month on a $200,000 house.
This is the amount of your monthly gross income that goes toward paying off your debts. It is also known as your debt-to-income ratio (DTI). Those include things like minimum credit card payments, child support, alimony, and installments on auto loans, student loans, and personal loans.
Mortgage lenders use your DTI ratio as a benchmark for affordability. The higher your existing debts are, the less monthly income you have to spare. That will affect how large of a mortgage payment you can afford.
- In the above example, a person with an annual income of around $70,000 and no other debts might be able to get a $200,000 mortgage loan.
- If that same borrower has a $1,000 debt payment, like a student loan or car payment, they will need to make about $88,000 a year to be able to get that $200K loan.
Your DTI is made up of two parts: front-end ratio and back-end ratio. As a rule of thumb, back-end ratio is the more important of the two. And lenders prefer it to be no greater than 36% for most mortgage programs but some may go up to 43%. By paying down your total debt before you buy a home — and avoiding taking on new debts — you can lower your DTI. This could substantially increase your home buying budget.
How much Income do I need to buy a $200k house? #200k #realestate #realestateinvesting
FAQ
What income is needed for a 200K mortgage?
Most of the time, you need an annual income of $50,000 to $70,000 to be able to afford a $200,000 mortgage. However, this can change depending on your other debts, down payment, and interest rates.
How much do I need to make to get a $200,000 loan?
Key Takeaways. The salary needed to buy a $200,000 home ranges from about $55,000 to $97,000 at current mortgage rates, depending on the down payment, insurance and other variables. The general rule that mortgage lenders follow is that your monthly mortgage payment shouldn’t be more than 18% of your gross household income.
Can I afford a 200K house on 50k a year?
If you make $50,000 a year, you might be able to buy a house worth between $180,000 and almost $258,000. That’s because your annual salary isn’t the only variable that determines your home buying budget. You also have to consider your credit score, current debts, mortgage rates, and many other factors.
How much do I need down for a 200K house?
To purchase a $200,000 house, you need a down payment of at least $40,000 (20% of the home price) to avoid PMI on a conventional mortgage.Apr 24, 2025
