Only about 266 percent of financed cars go to borrowers with credit scores of 661 or higher, but people with lower scores do have options.
Many, or all, of the products featured on this page are from our advertising partners who compensate us when you take certain actions on our website or click to take an action on their website. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and heres how we make money.
If youre looking to buy a car, the process could get more expensive soon. The Trump administrations tariffs could affect the auto industry, driving up prices. Knowing your credit score now can help you enter the buying process on strong footing.
The credit bureau Experian found in a report for the first quarter of 2020 that about 2066 percent of financed cars were for people with credit scores of 661 or higher (Experian Information Solutions). State of the Automotive Finance Market Q1 2025. Accessed Jun 9, 2025. View all sources. The report also found that on average, the credit score for a used-car loan was 684, while the average score for a new-car loan was 756.
Buying a car is an expensive endeavor that often requires financing. With the average new car price reaching over $47,000 in 2021, most buyers need a loan to afford the full cost Your credit history plays a major role in qualifying for an auto loan and securing a competitive interest rate So is a 690 credit score good enough to get approved and find a good deal?
Understanding Credit Scores for Auto Loans
Credit scores tell lenders how risky it is to lend money to you. Generally, the higher your score, the better interest rate you can get. The most common credit scoring models for auto loans are
-
It ranges from 250 to 900 and is best used for making decisions about auto loans. Many lenders rely on this specialized score.
-
FICO Score: Ranges from 300 to 850, the base FICO model used for most credit decisions. Versions 8 and 9 are common for auto lending.
-
VantageScore: Ranges from 300 to 850, a model developed by the three major credit bureaus as an alternative to FICO.
So where does a 690 score land you with these models?
-
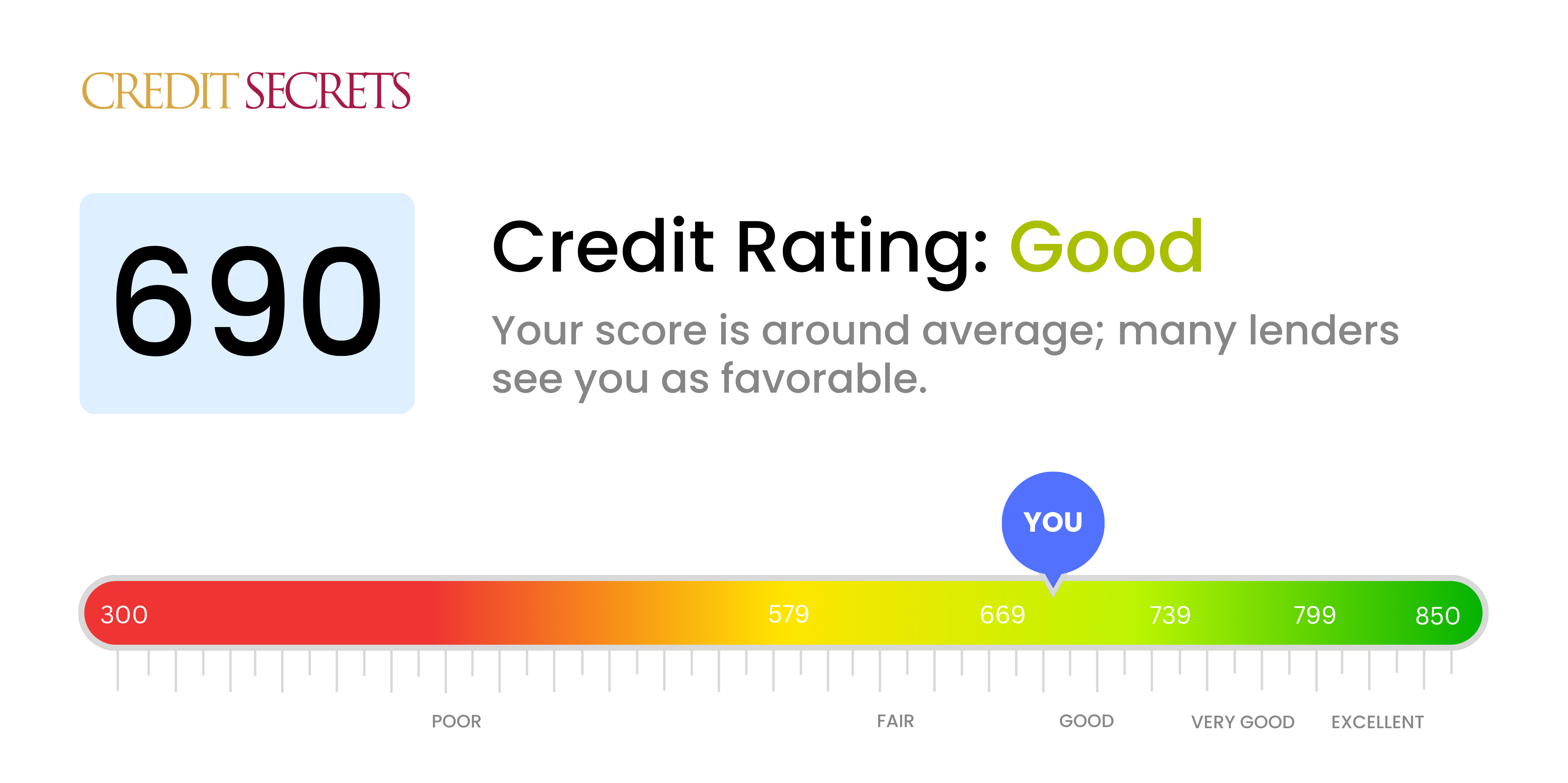
On the FICO Score range, 690 is considered “Fair” credit, below the “Good” range of 670-739.
-
For the VantageScore, a 690 is “Good” credit.
-
With the FICO Auto Score, 690 falls into the “Standard” credit tier.
Different lenders have different minimum scores, but in general, a score of 690 or higher is good credit for getting a traditional car loan. But if your score is 720 or higher, you’ll usually get better rates.
Interest Rates to Expect with a 690 Credit Score
The higher your credit score, the lower your interest rate. According to Experian data, here are the average new and used car loan rates for various credit tiers in Q1 2022:
| Credit Tier | New Car APR | Used Car APR |
|---|---|---|
| Super Prime (781-850) | 5.25% | 7.31% |
| Prime (661-780) | 6.87% | 9.36% |
| Non-Prime (601-660) | 9.83% | 13.92% |
| Subprime (501-600) | 13.18% | 18.86% |
| Deep Subprime (300-500) | 15.77% | 21.55% |
If your score is 690, you’re probably in the Non-Prime or Subprime rate range. You can expect to pay an APR of about 10% to 13% for a new car loan or between 4% and 19% for a used car loan. When you compare that to Prime borrowers with scores above 660, it’s pretty high.
Using a car loan calculator, we can see a 690 score adds over $2,000 in interest costs compared to a 720 score, assuming a $30,000 loan over 60 months:
- 690 credit score: 12% APR, $660 monthly payment, $11,571 total interest
- 720 credit score: 7% APR, $592 monthly payment, $9,487 total interest
Boosting your score before applying for an auto loan can translate to real savings.
Strategies to Improve Your Credit Score
If your score falls short of that “Prime” threshold, here are some tips to improve it:
-
Pay bills on time. Payment history is 35% of your FICO Score. Stay on top of due dates, or set up autopay.
-
Lower your credit utilization. Keep balances low compared to limits, ideally under 30%. This factor makes up 30% of your FICO Score.
-
Don’t close old accounts. Keeping your longest-open credit lines active helps the age of your credit history.
-
Mix up your credit types. Having installment loans like a mortgage plus revolving credit like cards helps your credit mix.
-
Dispute errors on your credit reports. Fixing mistakes directly boosts your score.
-
Become an authorized user. Being added to a spouse or family member’s old account can improve your score.
-
Limit new applications. Too many hard inquiries from applying for credit can ding your score temporarily.
With diligent credit management, you can boost your score significantly within 6-12 months.
Alternatives for Bad Credit Car Loans
For those with scores below 600, getting traditional financing can be challenging. Here are some options if you have “bad” credit but need a car:
-
Apply at subprime lenders: Specialty lenders like Capital One, AutoPay, and CARite cater to borrowers with bad credit. Rates are higher but they may approve those with poor scores.
-
“Buy here, pay here” dealers: These used car lots provide their own in-house financing for credit-challenged buyers. Down payments tend to be larger and interest rates very high.
-
Find a co-signer: Adding a co-signer with good credit can help you qualify and get better terms. Make sure the co-signer understands the risk they are accepting.
-
Save up a larger down payment: Putting 10-20% down shows lenders you are financially committed. A bigger down payment can help offset a lower score.
The Verdict: Is 690 a Good Credit Score for an Auto Loan?
While a FICO score of 690 is below the “Good” credit tier, it meets the minimum requirements for most standard car loans. But interest rates will likely be much higher than borrowers with “Very Good” (740+) or “Exceptional” (800+) credit.
Taking 6-12 months to improve your score before applying for an auto loan can potentially save thousands on interest costs over the loan term. Seeking out subprime lending options is an alternative if you need a car now with poor credit. But aim to build your score over time, so your next auto financing experience is less painful.
What minimum credit score is needed to buy a car?
There isn’t one specific score that’s required to buy a car because lenders have different standards. However, the vast majority of borrowers have scores of 661 or higher.
Borrowers with scores of 501 to 600 account for more than 15. 64% of cars financed, while people with scores of 500 or below account for 2. 39%, according to Experian.
A lower credit score won’t necessarily keep you from securing a car loan, but it might spike your interest rate, leading to higher payments.
How to buy a car with bad credit
If you are worried about getting a loan because your credit score is below 700, think about what you can offer the lender.
What Credit Score Do Car Dealerships Use? (Which Credit Bureau Is Most Used for Auto Loans?)
FAQ
What credit score is needed for a $25,000 car loan?
There’s no minimum credit score required to get an auto loan. However, a credit score of 661 or above—considered a prime VantageScore® credit score—will generally improve your chances of getting approved with favorable terms. For the FICO® Score Θ , a good credit score is 670 or higher.
Is 690 a good credit to buy a car?
According to Experian, a target credit score of 661 or above should get you a new-car loan with an annual percentage rate of around 6. 70% or better, or a used-car loan around 9. 06% or lower. Superprime: 781-850. 5. 18%.
What can a 690 credit score get you?
Even though a 690 credit score may result in more limited options for loans and credit cards, you may still be able to take out loans or apply for credit cards. Some lenders may require additional documentation or collateral, while others may offer higher interest rates or require a co-signer.
What credit score is needed for a $30,000 car?
To qualify for a $30,000 car loan, most lenders prefer to see a credit score of at least 660 to 700. That being said, your credit score is only one part of the equation. Lenders will also consider: Your debt-to-income ratio (how much you owe compared to how much you earn).
